CONCENTRIC STRANDING - A central wire or core surrounded by one or more layers of helically wound strands in a fixed round geometric arrangement. Generally each layer, after the first, has six more strands than the preceding layer and is applied in a direction opposite to that of the layer under it.
CONCENTRICITY - In a wire or cable, the measurement of the location of the center of the conductor with respect to the geometric center of the surrounding insulation.
CONCENTRICLAYCONDUCTOR - A single conductor composed of a central core surrounded by one or more helically laid wires. Each of these succeeding layers is applied with an opposite direction twist. The number of wires laid up the center wire is six, and each succeeding layer consists of six additional wires so that the number of wires in the strands are 7, 19, 37,61, etc.
COND. - Abbreviation for conductor. See conductor.
CONDUCTANCE - Symbol G. The measure of the ability of a substance to conduct electricity. The ratio of the current flow to the potential difference causing the flow. The real part of the admittance,
Y, which is given by:
|
|
Y = G + i B 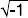 |
|
|
where B is the susceptance and i equals. |
|
|
|
For a direct current circuit, the conductance is the reciprocal of resistance and is measured in ohms. For a circuit containing both resistance,
R, and reactance,
X, the conductance is given by:
G = R / (R2 + X2)
CONDUCTIVITY - The capability of a material to carry electrical current, usually expressed as a percentage of copper conductivity (copper being 100%). The reciprocal of resistivity.
CONDUCTOR - A material that offers a low resistance to the passage of electric current (see resistivity). When a potential difference is applied across it, a relatively large current flows. A conductor usually consists of copper, aluminum, steel, silver, or other materials. Abbreviated as cond.
CONDUIT - A tube or trough for protecting electrical wires or cables.
CONNECTOR - A mechanism used to unite two pieces of cable, both physically and electrically.
CONSERVATION OF ENERGY PRINCIPLE - A principle in physics; the total energy of an isolated system remains constant irrespective of whatever internal change may take place with energy disappearing in one form and reappearing in another.
CONST. - Abbreviation for construction.
CONSTANTAN - An alloy of 55% copper and 45% nickel used in thermocouple with copper in the temperature range of 169° C to 386° C. Temperature coefficient of electrical resistivity, 0.0002 / ° C.